|
|
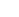
The forecasted pressure gradient (unit hectopascal, hPa) between Lugano and Zurich, on the basis of the MOS-data of the ECMWF-model, shows the flow over the Alps. If we have a negative pressure gradient, that means the surface pressure in Zurich is higher than in Lugano, north foehn comes up over the Alps (wind from north).
|
|
|
La prévision de la différence de pression (en hectopascal, hPa) entre Lugano et Zürich détermine le courant sur les Alpes. Si la différence de pression est négative, cette dernière sera plus basse à Lugano et plus haute à Zürich ce qui développera un courant de foehn du nord. Dans le cas contraire on aura du foehn du sud. Plus la différence de pression sera grande, plus le courant sera fort.
|
|
|
Die Vorhersage der Druckdifferenz in Hektopascal [hPa] zwischen Lugano und Zürich basiert auf dem statistischen Prognoseverfahren MOS von MeteoGroup und wird stündlich aufdatiert. Die Druckdifferenz gibt an, welche Windverhältnisse über den Alpen zu erwarten sind. Ist die Druckdifferenz positiv, d.h. Zürich hat den tieferen Druck als Lugano, so kann mit Südföhn über den Alpen gerechnet werden. Im umgekehrten Fall stellt sich Nordföhn ein. Je grösser die Druckdifferenz ist, umso stärker sind die Föhnwinde.
|
|
|
La previsione della differenza barica (unità ettopascal, simbolo hPa) tra Lugano e Zurigo per i prossimi 5 giorni si basa sul metodo statistico MOS di MeteoGroup e viene attualizzata ogni ora. La differenza barica è un indice delle correnti fra un versante delle Alpi e l'altro. Se la differenza risulta negativa, la pressione a Zurigo è più alta rispetto a Lugano.
|